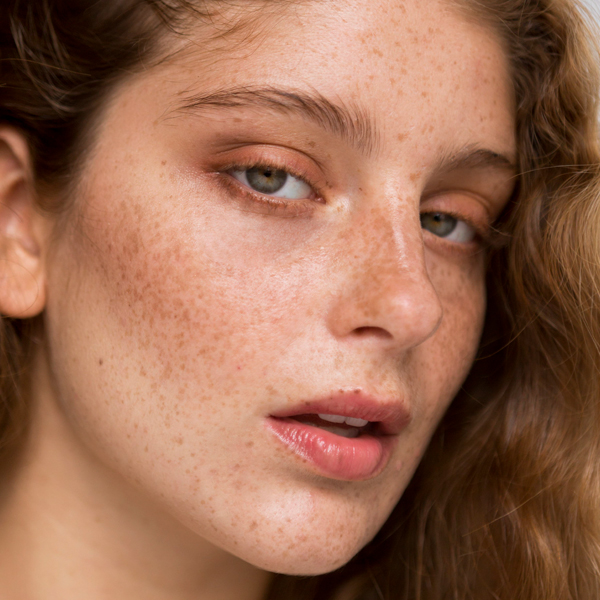
What is Pigmentation ?
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, hair, and eyes, primarily determined by the amount and type of melanin produced in the body. Melanin is the pigment responsible for the color of skin, hair, and eyes, and various factors influence its production.
When there's an overproduction or underproduction of melanin in certain areas of the skin, it can lead to uneven pigmentation. These pigmentation issues typically present as dark spots, patches, or lightened areas on the skin. Conditions like hyperpigmentation (excessive melanin) and hypopigmentation (lack of melanin) are the most common pigmentation disorders.
Types of Pigmentation Disorders
Hyperpigmentation
This occurs when there is too much melanin in certain areas of the skin,
resulting in darker spots or
patches.
Common forms of hyperpigmentation include
Sunspots(Age Spots)
Dark patches caused by sun exposure, usually seen on the face, hands, or shoulders.
Melasma
Large, dark patches often found on the face, commonly triggered by hormonal changes (pregnancy or birth control).
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Dark spots or scars left behind after an injury, acne, or other skin inflammation.
Hypopigmentation
This is when there is too little melanin in certain areas of the skin,
leading to lighter patches or spots.
Examples of hypopigmentation include
Vitiligo
A condition where patches of skin lose pigmentation, resulting in white spots due to the immune
system attacking pigment-producing cells (melanocytes).
Albinism
A genetic condition that results in a lack of melanin production, leading to lighter skin, hair, and
eyes.
Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation
Light spots may occur after a skin injury or infection heals.
Vitiligo
A condition where patches of skin lose pigmentation, resulting in white spots due to the immune system attacking pigment-producing cells (melanocytes).
Albinism
A genetic condition that results in a lack of melanin production, leading to lighter skin, hair, and eyes.
Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation
Light spots may occur after a skin injury or infection heals.
What Causes Pigmentation?
Several factors can contribute to changes in skin pigmentation, whether it’s an increase or decrease in melanin production. The key causes of pigmentation issues are:
Sun Exposure
- UV radiation from the sun triggers melanin production in the skin as a protective response. Prolonged sun exposure can lead to sunspots or age spots, areas where melanin accumulates.
- Sun damage over time can also cause uneven pigmentation, leading to the development of dark spots or freckles.
- In some cases, melasma can occur due to sun exposure, especially in individuals already predisposed to the condition.
Hormonal Changes
- Hormonal fluctuations can significantly affect pigmentation. This is commonly seen in conditions like melasma (also called the "mask of pregnancy"), where darker patches appear on the face, particularly around the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip.
- Pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can all trigger melasma in susceptible individuals.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also contribute to hormonal imbalances that lead to pigmentation changes.
Inflammation and Skin Injury
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a common cause of dark spots that occur after a skin injury, acne, rash, or any other form of inflammation.
- When the skin is injured or inflamed, it produces more melanin as part of the healing process, which can result in dark spots after the injury has healed.
- Similarly, post-inflammatory hypopigmentation can occur when the skin loses pigment after a burn, rash, or injury.
Genetics
- Genetics plays a significant role in how your skin responds to sunlight, hormonal changes, and other environmental factors. Some people are genetically predisposed to conditions like melasma, freckles, or age spots.
- Certain genetic conditions, like vitiligo or albinism, can cause either a loss of pigmentation or lighter skin tones.
Age
- As we age, the skin's ability to produce and distribute melanin becomes less efficient, leading to the appearance of age spots or sunspots.
- These dark spots often develop due to accumulated sun exposure over the years.
Medications
- Certain medications, including birth control pills, antibiotics, chemotherapy, and anti-seizure drugs, can cause pigmentation changes, either by increasing melanin production or causing skin discoloration.
- Some medications may make the skin more sensitive to the sun, increasing the risk of pigmentation disorders.
Diet and Lifestyle
- Poor diet or lack of nutrients can sometimes contribute to pigmentation disorders. For example, a deficiency in vitamins C, E, or B12 may cause changes in skin pigmentation.
- Smoking and an unhealthy lifestyle can also worsen pigmentation issues due to their impact on skin health and blood circulation.
Skin Conditions and Disorders
- Certain skin conditions, like eczema, psoriasis, and acne, can trigger pigmentation changes due to inflammation or scarring.
- Seborrheic keratosis and lentigines (age spots) are also conditions that cause pigment changes.
Key Benefits of Million Fractional Therapy for Pigmentation
Reduces Dark Spots and Uneven Tone
By stimulating collagen production and breaking down excess melanin, Dermapen with Million Fractional Therapy lightens dark spots and promotes skin tone.
Improves Skin Texture
The microneedling process enhances skin texture, making the skin smoother and more radiant.
Reduces Dark Spots and Uneven Tone
The treatment helps rejuvenate the skin, promoting faster healing of pigmentation spots and preventing new discoloration.
Minimal Downtime
Dermapen4 is a non-invasive treatment with minimal downtime. Most patients experience redness for a few hours after treatment, with minimal recovery time.
Safe for All Skin Types
Dermapen4 is safe for all skin types, making it an ideal solution for various pigmentation issues.
Long-Lasting Results
With a series of treatments, patients can see long-term results, with pigmentation gradually fading and the skin tone becoming brighter.

Why Choose Dermapen with Million Fractional Therapy for Pigmentation?
Proven Results
Proven track record of reducing pigmentation, evening out skin tone, and rejuvenating the skin.
Non-Invasive
Unlike laser treatments or chemical peels, it is a non-invasive microneedling procedure that requires little to no downtime, making it an ideal option for busy individuals.
Safe and Effective
The treatment is safe for all skin types and addresses various pigmentation concerns, including sun damage, age spots, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Customizable Treatment
The device allows for precise control over needle depth, which can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each patient and their unique pigmentation concerns.